
Name of the schema that the column data type (the underlying type of the domain, if applicable) is defined in Name of the database that the column data type (the underlying type of the domain, if applicable) is defined in (always the current database) If the column has a domain type, the name of the domain, else null. If the column has a domain type, the name of the schema that the domain is defined in, else null. If the column has a domain type, the name of the database that the domain is defined in (always the current database), else null. Name of the collation of the column, null if default or the data type of the column is not collatable Name of the schema containing the collation of the column, null if default or the data type of the column is not collatable Name of the database containing the collation of the column (always the current database), null if default or the data type of the column is not collatable If no field restrictions were specified (that is, the interval accepts all fields), and for all other data types, this field is null.Īpplies to a feature not available in PostgreSQL (see datetime_precision for the fractional seconds precision of interval type columns)Īpplies to a feature not available in PostgreSQL If data_type identifies an interval type, this column contains the specification which fields the intervals include for this column, e.g., YEAR TO MONTH, DAY TO SECOND, etc. For all other data types, this column is null. If data_type identifies a date, time, timestamp, or interval type, this column contains the (declared or implicit) fractional seconds precision of the type for this column, that is, the number of decimal digits maintained following the decimal point in the seconds value. It can be expressed in decimal (base 10) or binary (base 2) terms, as specified in the column numeric_precision_radix. The scale indicates the number of significant digits to the right of the decimal point.
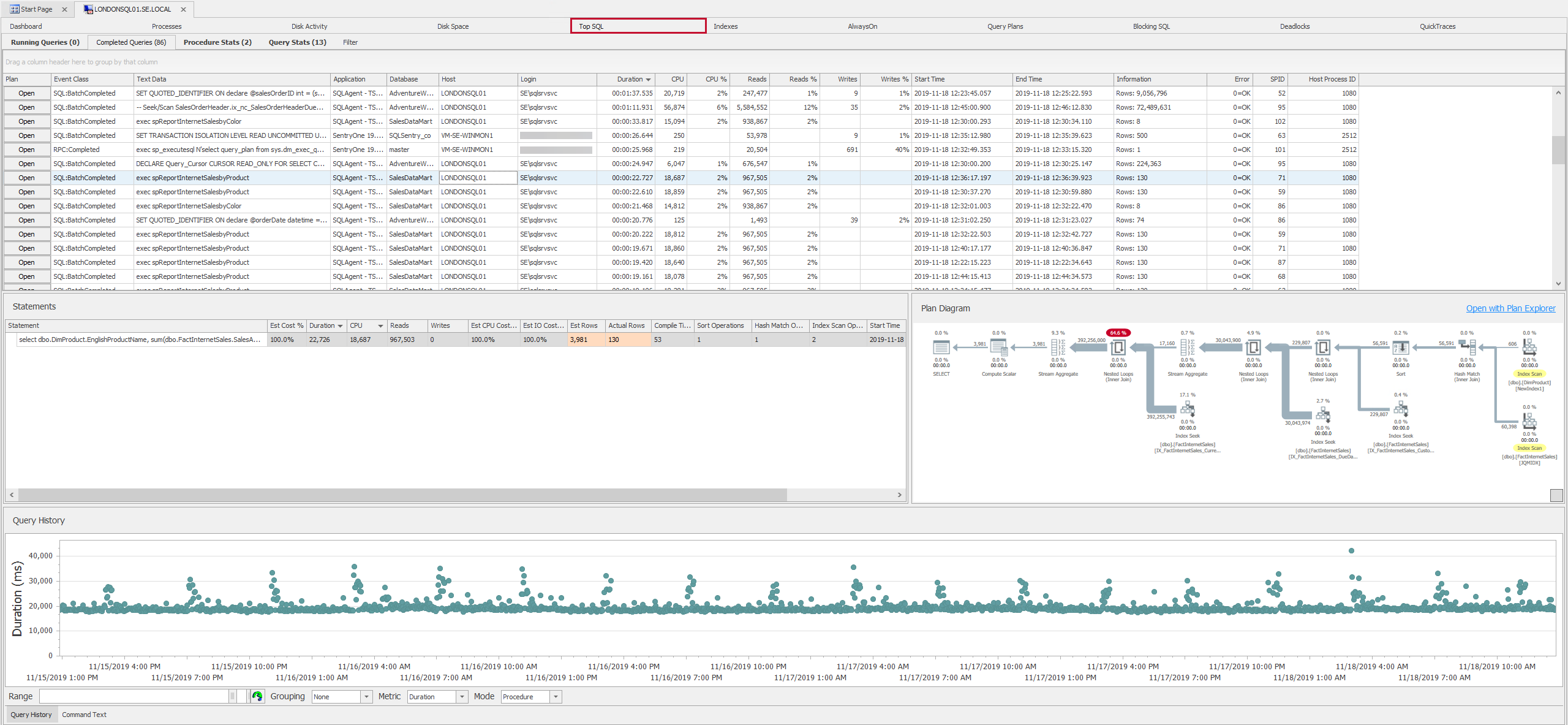

If data_type identifies an exact numeric type, this column contains the (declared or implicit) scale of the type for this column. If data_type identifies a numeric type, this column indicates in which base the values in the columns numeric_precision and numeric_scale are expressed.
The precision indicates the number of significant digits. If data_type identifies a numeric type, this column contains the (declared or implicit) precision of the type for this column. The maximum octet length depends on the declared character maximum length (see above) and the server encoding. If data_type identifies a character type, the maximum possible length in octets (bytes) of a datum null for all other data types. If data_type identifies a character or bit string type, the declared maximum length null for all other data types or if no maximum length was declared. If the column is based on a domain, this column refers to the type underlying the domain (and the domain is identified in domain_name and associated columns). A not-null constraint is one way a column can be known not nullable, but there can be others.ĭata type of the column, if it is a built-in type, or ARRAY if it is some array (in that case, see the view element_types), else USER-DEFINED (in that case, the type is identified in udt_name and associated columns). YES if the column is possibly nullable, NO if it is known not nullable. Ordinal position of the column within the table (count starts at 1)
Name of the database containing the table (always the current database)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
